- Foot and ankle are important structures of the body as they play vital role in locomotion & biomechanics of the body including posture.
- Foot is often the most neglected part of the body and is one of the commonest regions to get injuries due to sports, household falls, and vehicular accidents.
- Knowledge of biomechanics, pathologies and their proper treatment is vital for achieving good results in problems of foot & ankle.
Ankle Sprains:
- Ankle sprains are common ankle problems
- They are often associated with lateral or medial ankle ligamentous injuries and hence one can have associated pain, swelling or skin discolouration
- Ankle twisting injuries shouldn’t be neglected as the injuries can be associated with fractures around ankle joint
- Depending on the grades of injury the ankle ligament sprains can be treated in conservative manner using brace, bandages, cast or surgically i.e. ankle ligamentous reconstruction procedures.
- Ankle ligament reconstruction procedures can be either done arthroscopically or by open method.
Ankle Osteochondral Lesions
- Ankle osteochondral lesions (OCDs) mainly involve articular surface at the talus bone. Rarely it can be seen on the distal tibial articular surfaces.
- OCDs can occur as a result of twisting injuries to the ankle.
- Patients can present with problems such as pain, locking, & instability.
- Depending on size of the OCDs duration and locations, the OCDs can be treated either conservatively using physiotherapy, PRP injections etc. or surgically.
- Surgical treatment of ankle OCDs requires arthroscopic or open approach
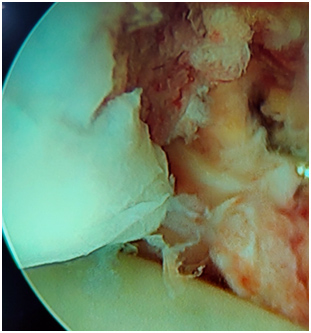
Ankle synovitis
- Ankle synovitis inflammation of the ankle joint synovium is a lining tissue of the joint capsules.
- It can present as ankle joint pain swelling, due to underlying conditions like infection, inflammation due to rheumatological conditions, such as various types of arthritis.
- Mostly management of ankle joint synovium involves management of underlying ethology such as rheumatological conditions etc .
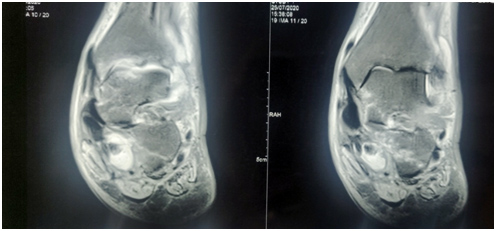
Ankle Arthritis:
- Ankle arthritis involves the tibiotalar joint. Associated arthritis of other adjacent joints such as subtalar joint, talonavicular or calcaneocuboid joints can be present.
- Leads to swelling, pain, restricted range of motion of the ankle.
- Often this issue can be treated conservatively in the initial phases with medications, orthoses and physiotherapy.
- In cases of advanced arthritis, patients may require either arthroscopy assisted or open ankle arthrodesis i.e. fusion or ankle replacement.
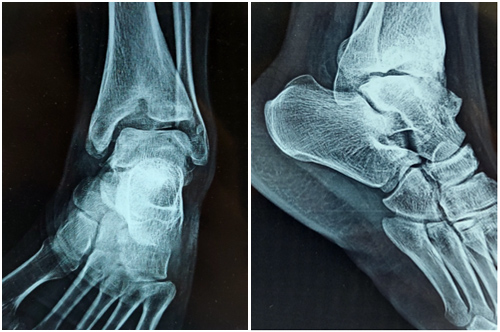
Achilles Tendon pain / rupture:
- Tendoachilles (TA) is a strong tendon, which inserts at the back of the heel.
- Because of trauma, repeated activities, underlying disorders like hypothyroidism diabetes etc. the tendoachilles can get damaged / swollen or sometimes can even rupture.
- Damage to tendoachilles leads to pain, swelling, difficulty in doing heel raises
- At the insertion on the heel, inflammation around tendoachilles can cause retrocalcaneal bursitis.
- Partial tears can be treated conservatively with medications, orthotics but complete tears may require repairs and augmentation
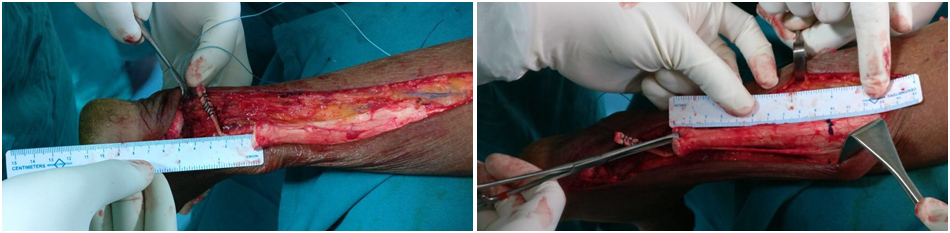
Flat Foot:
- Flat foot or pes planus is a well-known entity, commonly found in children.
- Similar conditions like forefoot pronation have similar clinical presentation.
- Absent or severely decreased medial arch of the foot is called the flat foot
- Patients often present with complaints of absent arch, abnormal gait pattern, abnormal callosities, pain on the medical aspect of the ankle.
- Initial management comprises of use of orthotics, physiotherapy, & medications.
- Severe flat foot with gross deformation may require surgical correction
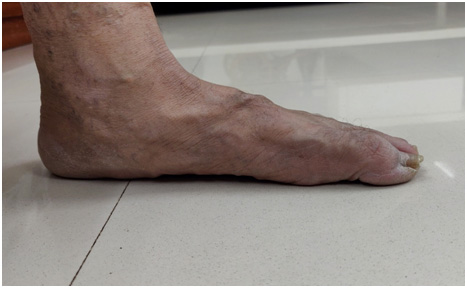
Bunion:
- Bunion is a bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of great toe, this is often secondary to conditions which involves maligned toes e.g. hallux valgus etc.
- Bunion may be asymptomatic or can be associated with swelling, redness, pain.
- If associated with decreased range of motion of the great toe, may suggest associated arthritis of the joint.
- Immunological conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, use of high heels etc, may be the under lying cause.
- Management usually requires proper shoe use, ant inflammatory medications, treatment of underlying pathologies.
Cavus foot:
- Can be considered as exact opposite condition than a flat foot. It’s a condition than the flat foot has excessively high arch. Its more pathological condition.
- Can be because of underlying neurological conditions such as polio, cerebral palsy, spina bifida and is likely to worsen progressively, hence early diagnosis & management is important.
- It can cause painful, swollen foots, hammer toes, unstable ankle etc.
- Usually it can be treated non-surgically using orthotics, medications etc. but those refractory to this treatment may require surgery.
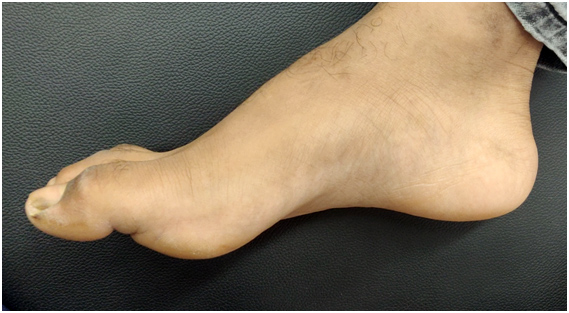
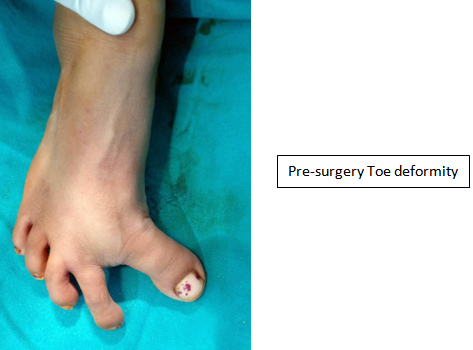
Toe Deformity:
- Apart from a ‘bunion’ other toe deformity are also common; they are hammer toes where toe bents at the proximal joint. It can lead to callosities, pressure sores etc. Inappropriate footwear usage may aggregate the condition.
- Mallet toe is a distally bent toe mainly seen on the 2nd, 3rd toe sides.
- Claw toes are toes which are bent both proximally and distally. They may be tell-tale sign of an underlying neurological condition and hence should be treated with precautions, and should be thoroughly investigated.
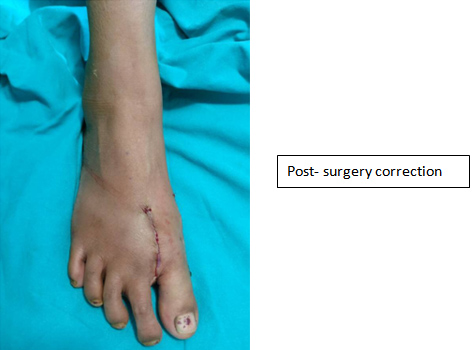
Neuromas:
- Neuroma means a soft tissue swelling around a nerve which can lead to nerve irritation and symptoms like pain, burning sensations etc.
- Morton’s neuroma is a condition which affects foot. Most commonly seen in the area between 3rd & 4th toes.
- Use of high heels, cavus feet etc. are few causative factors linked to the Morton’s neuroma.
- Initially they van be managed by using medications, orthotics, etc. & if patient persists to have complaints can be treated with local injections or surgery.
Fractures around ankle & foot:
- Fractures around the ankle involves medial or lateral malleolus, posterior malleolus, talus and calcareous.
- Foot fractures involve metatarsal and phalange fractures.
- Being a weight bearing region, these lead to inability to bear weight, early deformities etc.
- Anatomical reduction & fixation of these is required for better function.
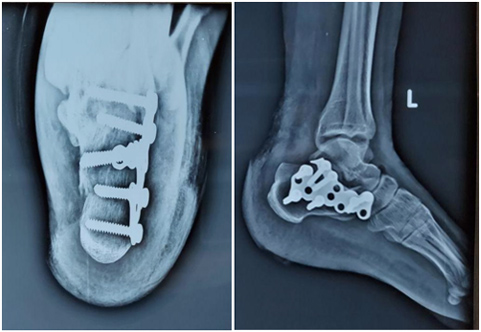
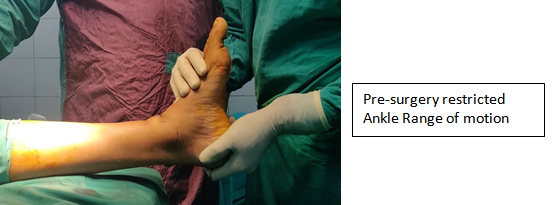
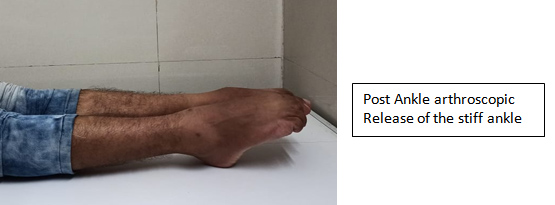
Stiff Ankle:
- A stiff ankle can be a sequel of trauma, malunited fractures, rheumatoid or osteoarthritis.
- Intraarticular damage to the cartilage can lead to decreased range of motion, progressive degeneration of the ankle.
- Early and aggressive physiotherapy after prolong immobilization can prevent development of the stiff ankle.
- Conservative management includes physiotherapy; while surgically it can be treated with either arthroscopic or open procedure i.e. Adhesiolysis
Dr. Sagar Kakatkar is well-known Foot and Ankle Surgeon in Nashik . he has experience of many successful foot and ankle surgeries. He provides effective and relieving treatment for your joints problems.
FAQs
For how long do I require footwear modifications for flat foot?
Modifications such as medial arch supports although don’t have proven curative value, they definitely help maintaining biomechanical alignment. So, their use has to be continued along with a few exercises.
My child doesn’t put his foot down properly. What should I do?
You will have to see a consultant. Children usually have different patterns of walking which may be physiological but sometimes they are pathological and may require treatment.
Is Elastocrep bandage the treatment for ankle sprain?
Bandaging definitely has a role in ankle ligament sprains but a lot depends on the degree of the sprains and severity of other injuries. If you have a gross ligamentous instability, you may not improve only with the bandaging.
When will I be able to go back playing sports after my foot surgery?
You will have to go through precise physiotherapy regimen which will also involve a gym protocol. But usually you will be able to go back to your sports activities in 8-9 months. if you consult with Foot and ankle surgeon in nashik then he will surely guide you best treatment to your feet & joints problems.
Do heel bone spurs reduce in size?
Heel spurs don’t reduce in size on their own. They may increase in size. But size of the spurs may not always correlate with the pain intensity.